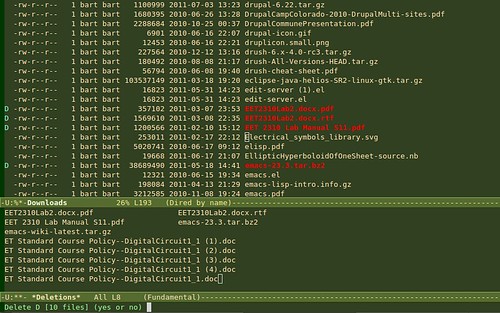
Delete some files in the Downloads folder
My Downloads folder is always out of control. There are always a ton of pdf files that I opened once in a browser but don't need to save. It's a pain to open a GUI file navigator, like Nautilus, and double click on each pdf file to view it and see if it should be tossed. However with Emacs, trimming my Downloads directory of old files is quick and easy.
Viewing Pdfs in Emacs
If you see a pdf with an uninformative name like 2010-09.pdf just hit <enter> when the cursor is on the file name, (when the file name is at point). Emacs will open the pdf in a new buffer. Once you have viewed the pdf and have decided its face you can quickly kill the pdf buffer with 'k' and you'll be returned to the directory. Now, if the pdf is unimportant, queue it to be deleted with 'd'. If you want to keep the file, but give it a better name, type 'R' to rename it. To unqueue a file for deletion, use 'u'. And finally to delete all the files currently queued for deletion, type 'x'.
Delete old Emacs backup files
If you have a lot of backup files that emacs created with ~ appended to the file name, you can quickly queue them all for deletion by typing '~'.
Here's the List of Directory Organizing Commands
| key combo | command |
|---|---|
| <enter> | open file at point |
| d | Queue File For Deletion |
| u | Unqueue File |
| ~ | Queue Backup Files for Del |
| x | eXecute Queued Delete Jobs |
| R | Rename File |
| k | Kill PDF Buffer |
Edit Zip'd or Tar-gz'd archives in place
If you need to edit a file inside a zip or tar archive, simply open the archive by hitting <enter> on the name in Dired mode, then click on the file. Edit the file and save it with 'C-x C-s', and then do another C-x C-s inside the zip buffer to save the archive with the file changes. The archive will be compressed again with your changes.
OMG!: Change File Owner, Group, Mode
| key combo | command |
|---|---|
| O | change owner |
| M | change mode |
| G | change group |
| Z | compress file |
Encrypt, Decrypt Files
Use ':e' to encrypt the file at point. Emacs will ask who you want to encrypt the file for (ie whose public key to use to encrypt the file.) You can also encrypt the file symmetrically with a password. Once the file is encrypted, there will be two files in the directory: the original file and the encrypted file with '.gpg' added to the file name.
Decrypt
To open the symmetrically encrypted file, click on its name and you will be prompted for a password. You can also type ':d' when the filename is at point.
EasyPG Assistant Docs
The program that is used to encrypt the file's is EasyPG Assistant. EasyPG Assistant Manual
Get More Help
Type 'C-hm' (describe mode) while in dired-mode, to pop open a help buffer, with a description of dired mode and a list of commands.
All Key Combinations named in post
| key combo | command |
|---|---|
| d | mark file for deletion |
| u | unmark file |
| x | eXecute queued deletions |
| R | rename/move file |
| O | change owner |
| M | change mode |
| G | change group |
| Z | compress file |
| y | show only certain file type |
| w | copy file name |
| RET | open file at point |
| k | if in pdf buffer, kill |
| C-x C-s | Save file or archive |
| i | insert sub-directory |
| ~ | mark all backup files for deletion |